Difference between revisions of "MagnetoDB"
m (→Authorization) |
m (→Table CRUD operations) |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
=== Table CRUD operations === | === Table CRUD operations === | ||
| + | With following methonds you can create, list, delete tables. | ||
| + | In the first implementation the througput configuration parameters can be ignored. So UpdateTable operation turns making no effect, because of that. | ||
| + | |||
* [http://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/APIReference/API_ListTables.html ListTables] | * [http://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/APIReference/API_ListTables.html ListTables] | ||
* [http://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/APIReference/API_DescribeTable.html DescribeTable] | * [http://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/APIReference/API_DescribeTable.html DescribeTable] | ||
Revision as of 23:57, 29 October 2013
Status
Scope
Document describes the idea and technical concept of DB service for OpenStack like Amazon DynamoDB. There is no implementation yet.
What is MagnetoDB?
MagnetoDB is Amazon DynamoDB API implementation for OpenStack world.
What is DynamoDB?
DynamoDB is a fast, fully managed NoSQL database service that makes it simple and cost-effective to store and retrieve any amount of data, and serve any level of request traffic. With DynamoDB, you can offload the administrative burden of operating and scaling a highly available distributed database cluster
DynamoDB tables do not have fixed schemas, and each item may have a different number of attributes. Multiple data types add richness to the data model. Local secondary indexes add flexibility to the queries you can perform, without impacting performance. [1]
Why it is needed?
In order to provide hight level database service with DynamoDB API interface for OpenStack users.
Just simply create the table and start working with your data. No vm provisioning, database software setup, configuration, patching, monitoring and other administrative routine.
Integration with Trove?
Initially suggested as blueprint for Trove it was rejected as not following the programm mission.
MagnetoDB is not one more database, which can be provisioned and managed by Trove. It is one more OpenStack service with own API, keystone based authentication, quota management.
However, the underlaying database will be provisioned and managed by Trove, in order to reuse existing Openstack components and avoid duplication of functionality.
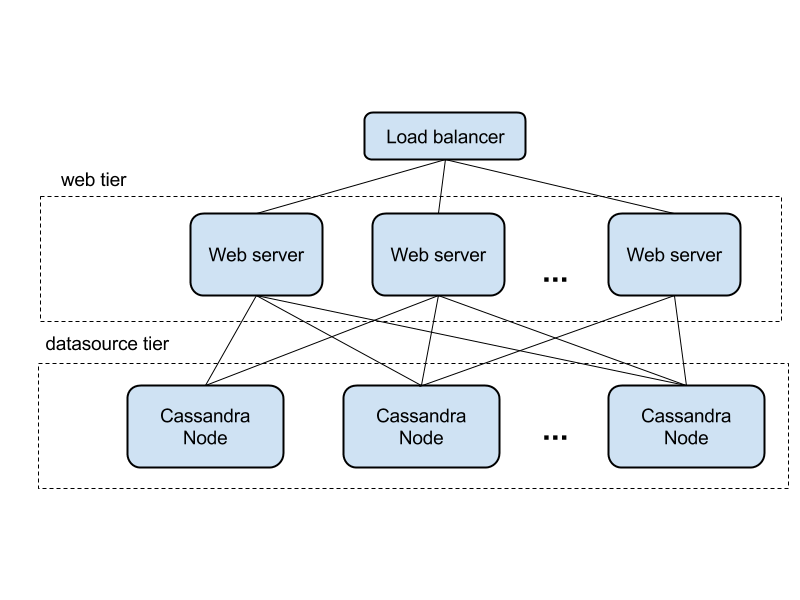
Overall architecture
The shape of the architecture based on Cassandra storage is below. It is the classic 2 layer web application, where each layer is horizontally scalable. Requests are routed by load balancer to web application layer, and processed there.
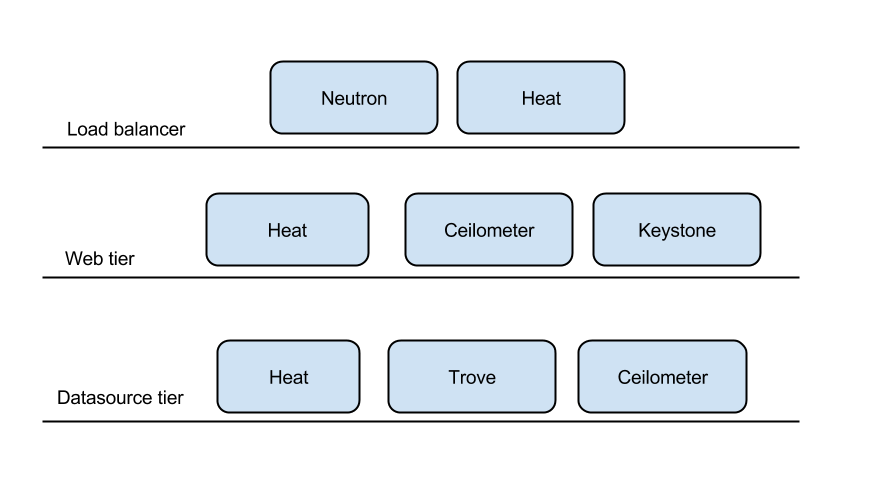
In projection to existing OpenStack components
API
The DynamoDB API documented very well here Operations in Amazon DynamoDB However, the key aspects are mentioned below.
The API present HTTP request/responce, where JSON is used as data transfer model. The request body contains the payload, and HTTP headers are used for metadata.
Example of such request
POST / HTTP/1.1 host: dynamodb.us-west-2.amazonaws.com x-amz-date: 20130112T092034Z x-amz-target: DynamoDB_20120810.CreateTable Authorization: AWS4-HMAC-SHA256 Credential=AccessKeyID/20130112/us-west-2/dynamodb/aws4_request,SignedHeaders=host;x-amz-date;x-amz-target,Signature=145b1567ab3c50d929412f28f52c45dbf1e63ec5c66023d232a539a4afd11fd9 content-type: application/x-amz-json-1.0 content-length: 23 connection: Keep-Alive
As you can see the operation name and authorization data is sent in HTTP request headers.
Authorization
It is HMAC based on EC2 Credentials, which is sent in a header of HTTP request as in example above.
Table CRUD operations
With following methonds you can create, list, delete tables. In the first implementation the througput configuration parameters can be ignored. So UpdateTable operation turns making no effect, because of that.
Item CRUD operations
Data quering
Batch operations
Implementation
Pluggability
The most suitable data source is Cassandra. But it is better to make datasource plugguble and give the framework for implementation of interface for any other underlying storage.
OpenStack component reusage
| Purpose | OS component |
|---|---|
| Provisioning of web tire | Heat, Mistral (Convection) |
| Load balancer | LBaaS, Neutron |
| Autoscaling of web tier | Heat autoscaling, Ceilometer |
| Data Source provisioning and management | Trove |
| Monitoring | Ceilometer |
| Authentication | Keystone |
Autoscaling
- Web autoscaling is suggested to implement with HEAT autoscaling group resource
- Datasource scalability based on future Trove autoscaling