Difference between revisions of "Cinder/NewLVMbasedDriverForSharedStorageInCinder"
< Cinder
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | = | + | = Support LVM on a volume attached to multiple nodes = |
== Related blueprints == | == Related blueprints == | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Goals == | == Goals == | ||
| − | * | + | * The goal of this blue print is to support LVM on a volume attached to multiple nodes. |
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
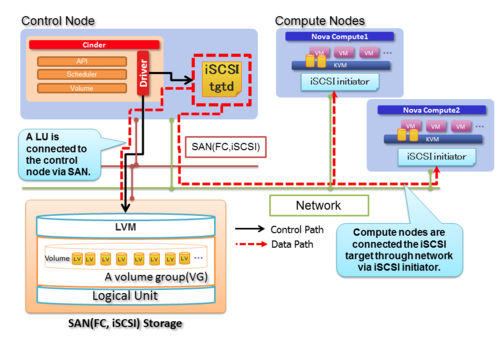
| − | + | Current LVM driver only supports iSCSI topology and a guest instance on nova compute is connected to a LV on a volume-group via iSCSI target. | |
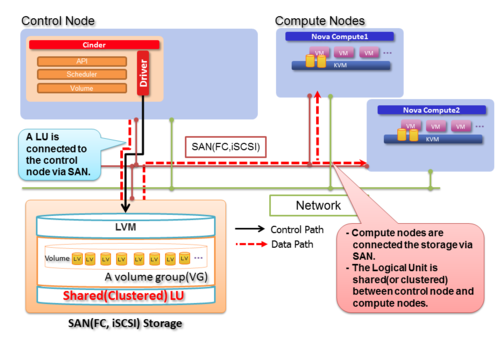
| − | In | + | In FC storage environment, when a volume on the storage is attached to multiple servers such as cinder node and compute nodes, these nodes can access a single volume-group on the volume simultaneously. So every LV on the volume-group is visible on each node. |
| + | Using this configuration, a guest instance will be able to transport data through a guest instance to LVs on cinder volume via FC directly instead of iSCSI target. | ||
| − | === (a) | + | |
| + | === (a) Existing iSCSI LVM driver === | ||
[[File:StandardLVM.png|border|500px|Standard iSCSI LVM driver]] | [[File:StandardLVM.png|border|500px|Standard iSCSI LVM driver]] | ||
| − | === (b) LVM | + | === (b) Suggesting LVM driver === |
[[File:NewLVMbasedDriverForSharedStorage.png|border|500px|LVM-based driver for shared storage]] | [[File:NewLVMbasedDriverForSharedStorage.png|border|500px|LVM-based driver for shared storage]] | ||
== Benefits of this driver == | == Benefits of this driver == | ||
| − | # | + | # Better I/O performance and latency for guest instances |
| − | # Less network traffic of data transfer between | + | # Less network traffic of data transfer between cinder node and compute nodes |
| − | # Basic features of | + | # Reduce work load of cinder node |
| + | # Basic features of cinder such as snapshot and backup etc. are appreciable from existing cinder LVM driver. | ||
== Basic Design == | == Basic Design == | ||
| − | * This driver uses | + | === Multiple attached volume === |
| − | + | * This driver uses LVM on a volume attached to multiple nodes. By using LVM on multiple attached volume, cinder node and compute nodes can access access a single volume-group on the volume simultaneously. So every LV on the volume-group is visible on each node. | |
| − | * LVM holds management region including metadata of | + | * A volume-group on multiple attached volume is necessary to prepare previously. The driver creates LV as a cinder volume from the volume-group. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Exclusive access control for metadata === | ||
| + | * LVM holds management region including metadata of volume-group configuration information. If multiple nodes update the metadata simultaneously, the metadata will be broken. Therefore, exclusive access control is necessary. Specifically, operation of updating metadata is permited only cinder node. | ||
| + | |||
* The operations of updating metadata are followings. | * The operations of updating metadata are followings. | ||
| − | ** Volume | + | ** Volume creation |
| − | *** When Cinder node create a new LV on a | + | *** When Cinder node create a new LV on a volume-group, metadata of LVM is renewed but the update does not notify other compute nodes. Only cinder node knows the update this point. |
| − | ** Volume | + | ** Volume deletion |
| − | *** Delete a LV on a | + | *** Delete a LV on a volume-group from Cinder node. |
** Volume extend | ** Volume extend | ||
| − | *** Extend a LV on a | + | *** Extend a LV on a volume-group from Cinder node. |
| − | ** Snapshot | + | ** Snapshot creation |
| − | *** Create a snapthot of a LV on a | + | *** Create a snapthot of a LV on a volume-group from Cinder node. |
| − | ** Snapshot | + | ** Snapshot deletion |
| − | *** Delete a snapthot of a LV on a | + | *** Delete a snapthot of a LV on a volume-group from Cinder node. |
* The operations without updating metadata are followings. These operations are permitted every compute node. | * The operations without updating metadata are followings. These operations are permitted every compute node. | ||
| − | ** Volume | + | ** Volume attachment |
| − | *** When attaching a LV to guest | + | *** When attaching a LV to guest instance on a compute nodes, compute node have to reload LVM metadata using "lvscan" or "lvs" because compute node does not know latest LVM metadata. After reloading metadata, compute node recognise latest status of volume-group and LVs. |
| − | *** And then, in order to attach new LV, compute nodes need to create a device file such as /dev/" | + | *** And then, in order to attach new LV, compute nodes need to create a device file such as /dev/"volume-group name"/"LV name" using "lvchane -ay" command. |
*** After activation of LV, nova compute can attach the LV into guest VM. | *** After activation of LV, nova compute can attach the LV into guest VM. | ||
| − | * Volume | + | * Volume detachment |
| − | ** After detaching a volume from guest VM, compute node deactivate the LV using " | + | ** After detaching a volume from guest VM, compute node deactivate the LV using "lvchange -an". As a result, unnecessary device file is removed from the compute node. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 67: | Line 75: | ||
* Use QEMU/KVM as a hypervisor (via libvirt compute driver) | * Use QEMU/KVM as a hypervisor (via libvirt compute driver) | ||
* Shared block storages between Cinder node and compute nodes via iSCSI or Fibre Channel | * Shared block storages between Cinder node and compute nodes via iSCSI or Fibre Channel | ||
| − | * A volume group on | + | * A volume group on a volume attached to multiple nodes |
| − | * | + | * Exclude target scsi device from lvmetad on compute nodes |
** When compute node attaches created volume to a virtual machine, latest LVM metadata is necessary. However the lvmetad caches LVM metadata and this prevent to obtain latest LVM metadata. | ** When compute node attaches created volume to a virtual machine, latest LVM metadata is necessary. However the lvmetad caches LVM metadata and this prevent to obtain latest LVM metadata. | ||
== Configuration == | == Configuration == | ||
| − | In order to enable | + | In order to enable LVM multiple attached driver, need to define theses values at /etc/cinder/cinder.conf |
Example | Example | ||
Revision as of 21:13, 27 March 2014
Support LVM on a volume attached to multiple nodes
Related blueprints
- https://blueprints.launchpad.net/cinder/+spec/lvm-driver-for-shared-storage
- https://blueprints.launchpad.net/nova/+spec/lvm-driver-for-shared-storage
Goals
- The goal of this blue print is to support LVM on a volume attached to multiple nodes.
Overview
Current LVM driver only supports iSCSI topology and a guest instance on nova compute is connected to a LV on a volume-group via iSCSI target.
In FC storage environment, when a volume on the storage is attached to multiple servers such as cinder node and compute nodes, these nodes can access a single volume-group on the volume simultaneously. So every LV on the volume-group is visible on each node.
Using this configuration, a guest instance will be able to transport data through a guest instance to LVs on cinder volume via FC directly instead of iSCSI target.
(a) Existing iSCSI LVM driver
(b) Suggesting LVM driver
Benefits of this driver
- Better I/O performance and latency for guest instances
- Less network traffic of data transfer between cinder node and compute nodes
- Reduce work load of cinder node
- Basic features of cinder such as snapshot and backup etc. are appreciable from existing cinder LVM driver.
Basic Design
Multiple attached volume
- This driver uses LVM on a volume attached to multiple nodes. By using LVM on multiple attached volume, cinder node and compute nodes can access access a single volume-group on the volume simultaneously. So every LV on the volume-group is visible on each node.
- A volume-group on multiple attached volume is necessary to prepare previously. The driver creates LV as a cinder volume from the volume-group.
Exclusive access control for metadata
- LVM holds management region including metadata of volume-group configuration information. If multiple nodes update the metadata simultaneously, the metadata will be broken. Therefore, exclusive access control is necessary. Specifically, operation of updating metadata is permited only cinder node.
- The operations of updating metadata are followings.
- Volume creation
- When Cinder node create a new LV on a volume-group, metadata of LVM is renewed but the update does not notify other compute nodes. Only cinder node knows the update this point.
- Volume deletion
- Delete a LV on a volume-group from Cinder node.
- Volume extend
- Extend a LV on a volume-group from Cinder node.
- Snapshot creation
- Create a snapthot of a LV on a volume-group from Cinder node.
- Snapshot deletion
- Delete a snapthot of a LV on a volume-group from Cinder node.
- Volume creation
- The operations without updating metadata are followings. These operations are permitted every compute node.
- Volume attachment
- When attaching a LV to guest instance on a compute nodes, compute node have to reload LVM metadata using "lvscan" or "lvs" because compute node does not know latest LVM metadata. After reloading metadata, compute node recognise latest status of volume-group and LVs.
- And then, in order to attach new LV, compute nodes need to create a device file such as /dev/"volume-group name"/"LV name" using "lvchane -ay" command.
- After activation of LV, nova compute can attach the LV into guest VM.
- Volume attachment
- Volume detachment
- After detaching a volume from guest VM, compute node deactivate the LV using "lvchange -an". As a result, unnecessary device file is removed from the compute node.
| Operations | Volume create | Volume delete | Volume extend | Snapshot create | Snapshot delete | Volume attach | Volume detach |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cinder node | x | x | x | x | x | - | - |
| Compute node | - | - | - | - | - | x | x |
| Cinder node with compute | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
Prerequisites
- Use QEMU/KVM as a hypervisor (via libvirt compute driver)
- Shared block storages between Cinder node and compute nodes via iSCSI or Fibre Channel
- A volume group on a volume attached to multiple nodes
- Exclude target scsi device from lvmetad on compute nodes
- When compute node attaches created volume to a virtual machine, latest LVM metadata is necessary. However the lvmetad caches LVM metadata and this prevent to obtain latest LVM metadata.
Configuration
In order to enable LVM multiple attached driver, need to define theses values at /etc/cinder/cinder.conf
Example
[LVM_shared] volume_group=cinder-volumes-shared volume_driver=cinder.volume.drivers.lvm.LVMSharedDriver volume_backend_name=LVM_shared