Difference between revisions of "Vitrage"
(→Development (Blueprints, Roadmap, Design...)) |
Alexey Weyl (talk | contribs) (→High Level Architecture) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| − | '''Vitrage | + | '''Vitrage Synchronizer''' |
| − | Responsible for importing information regarding the virtual | + | Responsible for importing information regarding all the components (physical, virtual, alarms, etc..). |
It collects this data from different sources, including (but not limited to) Openstack, and saves it in Vitrage Graph. | It collects this data from different sources, including (but not limited to) Openstack, and saves it in Vitrage Graph. | ||
| − | + | Many instances of the synchronizer can be used in Vitrage. They will all listen to the bus, but will perform actions according to the each ones purpose (this is made for scalability and performance issues). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''Vitrage Graph''' | '''Vitrage Graph''' | ||
| − | Representation of the different entities in the Cloud and their inter-relations. Relationships can range from the topological (e.g., which host a VM is hosted on) to the logical (e.g., one alert causes a different alert). | + | Representation of the different entities in the Cloud and their inter-relations. Relationships can range from the topological (e.g., which host a VM is hosted on) to the logical (e.g., one alert causes a different alert). It contains the graph DB itself and a collection of basic graph algorithms (e.g., sub-matching algorithms , BFS, DFS and etc). |
| Line 48: | Line 38: | ||
Coordinates the analysis of the Vitrage Graph and processes the results of this analysis. | Coordinates the analysis of the Vitrage Graph and processes the results of this analysis. | ||
| − | + | Responsible for execution different kind of actions on the vitrage graph, such as: | |
| − | Responsible for execution of the | ||
*RCA – Root Cause Analysis | *RCA – Root Cause Analysis | ||
*Deduce Alerts – Raise an alert as a result of other alert(s) or other events and changes in the Cloud | *Deduce Alerts – Raise an alert as a result of other alert(s) or other events and changes in the Cloud | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Vitrage Notifier''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Responsible to inform the different services with the Vitrage evaluator results. | ||
| Line 60: | Line 53: | ||
| − | '''Vitrage | + | '''Vitrage CLI''' |
| + | |||
| + | The CLI for Vitrage. Enables to receive information from the Vitrage Graph regarding the cloud and analysis related to root cause. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Vitrage UI''' | ||
| − | + | Enables the client to check and monitor the graph and RCA. | |
== Use Cases == | == Use Cases == | ||
Revision as of 05:55, 9 November 2015
Contents
What is Vitrage?
Vitrage is the Openstack RCA (Root Cause Analysis) Engine for organizing, analyzing and expanding OpenStack alarms & events, yielding insights regarding the root cause of problems and deducing the existence of problems before they are directly detected.
Mission & Scope
Vitrage is a project dedicated to making the events and alarms in OpenStack more meaningful and helpful. The ideal to which we strive is that every significant event in the system should have a timely alarm/event generated for it, that alarms are raised as early as possible after the event, and that the cause-effect relationships between different events is understood and visualized.
High Level Functionality
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA) for alarms/events
- Deduced alarms and states (i.e., raising an alarm or modifying a state based on analysis of system, not only direct monitoring)
- Alarm Aggregation (i.e., grouping alarms by categories, such as resources and severity, making them more manageable and understandable)
- Physical-to-Virtual entities mapping
- UI support for all features above
Design & Implementation
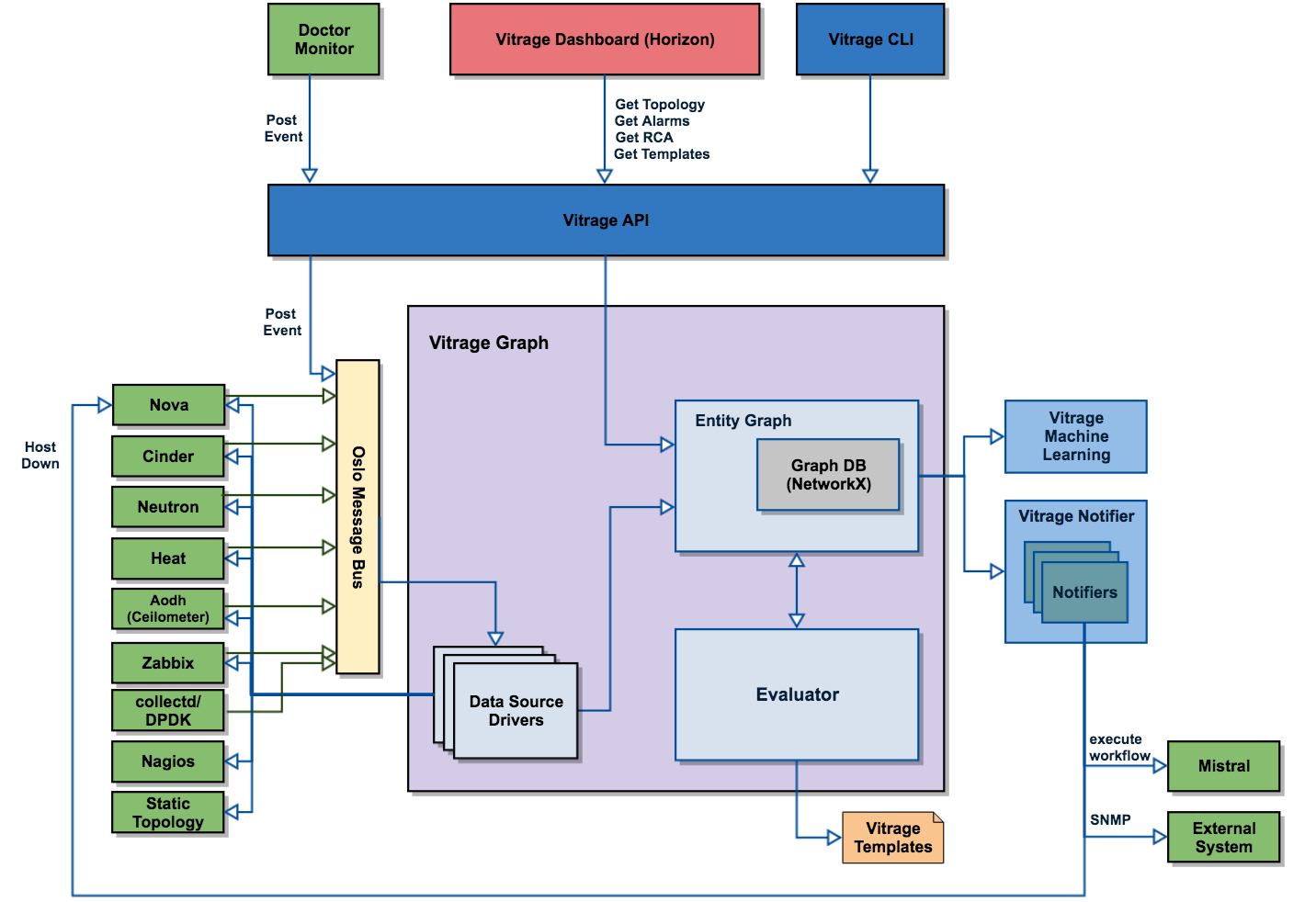
High Level Architecture
Vitrage Synchronizer
Responsible for importing information regarding all the components (physical, virtual, alarms, etc..). It collects this data from different sources, including (but not limited to) Openstack, and saves it in Vitrage Graph. Many instances of the synchronizer can be used in Vitrage. They will all listen to the bus, but will perform actions according to the each ones purpose (this is made for scalability and performance issues).
Vitrage Graph
Representation of the different entities in the Cloud and their inter-relations. Relationships can range from the topological (e.g., which host a VM is hosted on) to the logical (e.g., one alert causes a different alert). It contains the graph DB itself and a collection of basic graph algorithms (e.g., sub-matching algorithms , BFS, DFS and etc).
Vitrage Evaluator
Coordinates the analysis of the Vitrage Graph and processes the results of this analysis. Responsible for execution different kind of actions on the vitrage graph, such as:
- RCA – Root Cause Analysis
- Deduce Alerts – Raise an alert as a result of other alert(s) or other events and changes in the Cloud
Vitrage Notifier
Responsible to inform the different services with the Vitrage evaluator results.
Vitrage API
The API for Vitrage. Enables to receive information from the Vitrage Graph regarding the cloud and analysis related to root cause.
Vitrage CLI
The CLI for Vitrage. Enables to receive information from the Vitrage Graph regarding the cloud and analysis related to root cause.
Vitrage UI
Enables the client to check and monitor the graph and RCA.
Use Cases
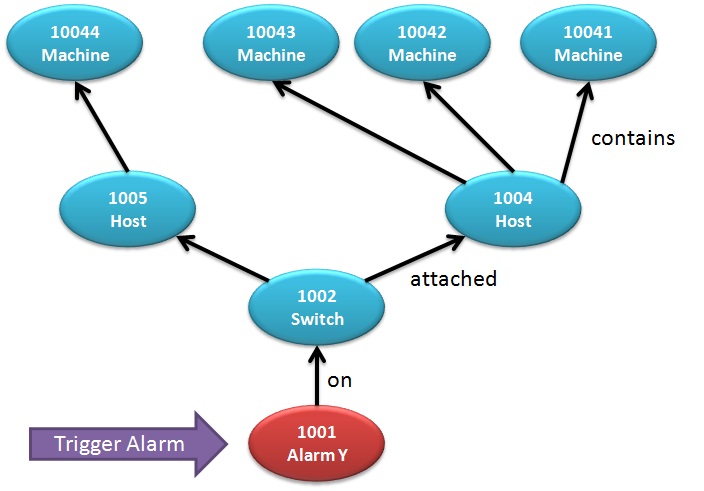
Baseline
We consider the following example, where a we are monitoring a Switch (id 1002), for example via Nagios test, and as a result an alarm is raised on a Switch. The following image depicts the logical relationship among different resources in the system that are related to this switch. Note the mapping between virtual (machine) and physical (host, switch) entities.
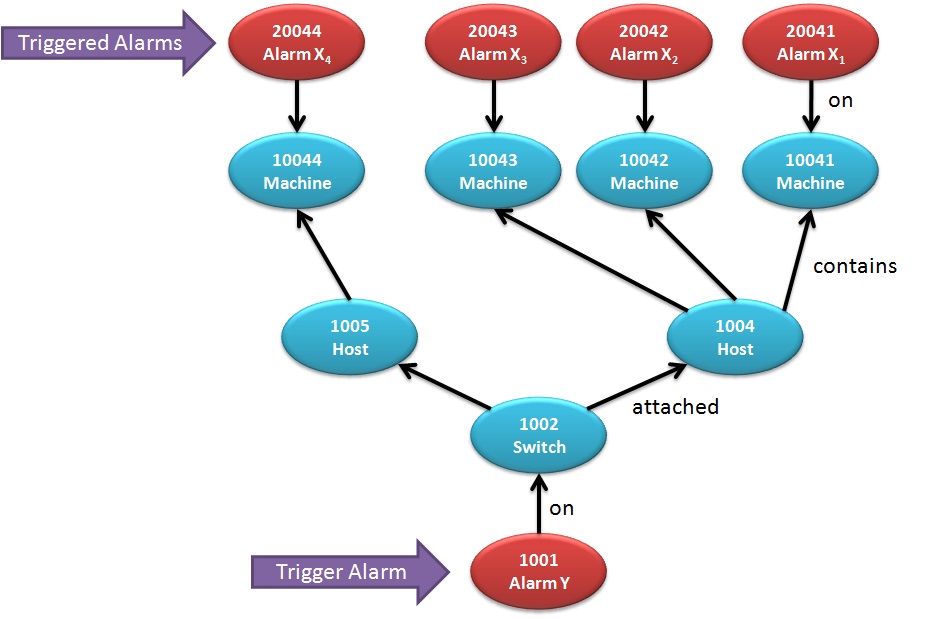
Deduced alarms & states
The problems on the switch can, at times, have a bad impact on the VMs running on hosts attached to the switch, and we would like to have an alarm on those VMs to indicate this, as shown here:
As can be seen, an alarm is raised on all VMs associated with the switch. Similarly, we could want the state of all VMs to be changed to "ERROR". We would like to be able to do this even if, perhaps due to the problem with the switch, we cannot directly monitor the state of the VMs, since we can deduce this problem from the state of the switch.
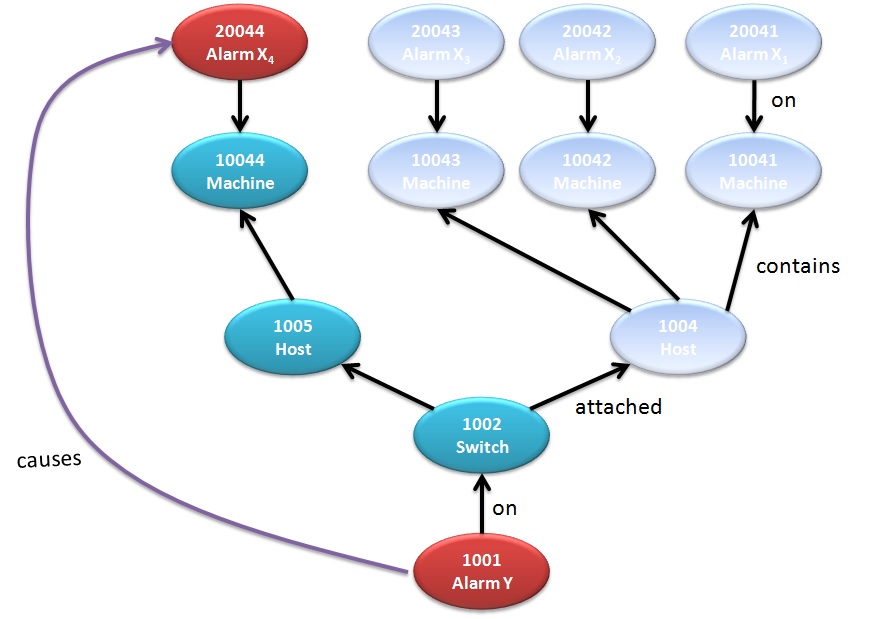
Root Cause Indicators
Furthermore, we would like to be able to track this cause and effect - that the problem in the switch caused a problem in the VMs. In the following image, we highlight a single connection between the cause and effect for clarity - but all such links will be supported.
Important Note: not all deduced alarms are caused by the trigger - the trigger might only be an indication of correlation, not causation. In the case we are examining, however, the trigger is also the cause:
Once the local "causes" links (one hop) are detected and registered, we can follow them one hop after another to track the full causal chain of a sequence of events.
Development (Blueprints, Roadmap, Design...)
- Contact persons:
- Alexey Weyl - alexey.weyl@alcatel-lucent.com
- Ifat Afek - ifat.afek@alcatel-lucent.com
- Elisha Rosensweig - elisha.rosensweig@alcatel-lucent.com
- Ohad Shamir - ohad.shamir@alcatel-lucent.com
- Vitrage Team
- Communication and Meetings
- Project at Launchpad: http://launchpad.net/vitrage
- IRC channel for regular daily discussions: #openstack-vitrage
- The weekly meeting of Nov 4 will be held on Wednesday at 9:00am UTC on IRC in #openstack-vitrage. We will update regarding the next meetings.
- Use [Vitrage] tag for Vitrage emails on OpenStack Mailing Lists
- Check Vitrage Meetings for more details
- Blueprints
- Source Code