Difference between revisions of "Rally"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| + | = Use Cases = | ||
| + | |||
| + | Use Cases: | ||
| + | # Investigate how deployments influence on OS performance (find the set of good OpenStack deployment architectures) | ||
| + | # Automatically get numbers & profiling info about how your changes influence on OS performance | ||
| + | # Using Rally profiler detect scale & performance issues. E.g. when we delete 3 VMs by one request they are deleted one by one because of [http://37.58.79.43:8080/traces/0011f252c9d98e31 | DB lock on quotas table] | ||
| + | # Determine maximal load that could handle production cloud | ||
| + | # Compare different Hardware, and find set of the best configurations | ||
| + | # Generate cloud specification. (Maximal load,) | ||
= Architecture = | = Architecture = | ||
Revision as of 21:18, 19 October 2013
Contents
Introduction
Rally is a Benchmark-as-a-Service project for OpenStack.
Rally is intended for providing the community with a benchmarking tool that is capable of performing specific, complicated and reproducible test cases on real deployment scenarios.
In the OpenStack ecosystem there are currently several tools that are helpful in carrying out the benchmarking process for an OpenStack deployment. To name a few, there are DevStack and FUEL which are intended for deploying and managing OpenStack clouds, the Tempest testing framework that validates OpenStack APIs, some tracing facilities like Tomograph with Zipkin, and so on. The challenge, however, is to compile all these tools together on a reproducible basis. That can be a rather difficult task since the number of compute nodes in a practical deployment can be really huge and also because one may be willing to use lots of different deployment strategies that pursue different goals (e.g., while benchmarking the Nova Scheduler, one usually does not care of virtualization details, but is more concerned with the infrastructure topologies; while in other specific cases it may be the virtualization technology that matters). Compiling a bunch of already existing benchmarking facilities into one project, making it flexible to user requirements and ensuring the reproducibility of test results, is exactly what Rally does.
Use Cases
Use Cases:
- Investigate how deployments influence on OS performance (find the set of good OpenStack deployment architectures)
- Automatically get numbers & profiling info about how your changes influence on OS performance
- Using Rally profiler detect scale & performance issues. E.g. when we delete 3 VMs by one request they are deleted one by one because of | DB lock on quotas table
- Determine maximal load that could handle production cloud
- Compare different Hardware, and find set of the best configurations
- Generate cloud specification. (Maximal load,)
Architecture
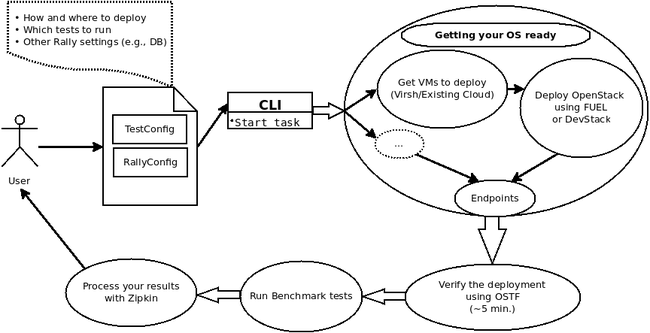
Rally is basically split into 4 main components:
- Deploy Engine, which is responsible for processing and deploying VM images (using DevStack or FUEL according to user’s preferences). The engine can do one of the following:
- deploying an OS on already existing VMs;
- starting VMs from a VM image with pre-installed OS and OpenStack;
- deploying multiply VMs inside each has OpenStack compute node based on a VM image.
- Server Provider, provides servers (virtual servers) to deploy OpenStack.
- Benchmarking Tool, which carries out the benchmarking process in several stages:
- runs Tempest tests, reduced to 5-minute length (to save the usually expensive computing time);
- runs a set of benchmark scenarios (using the Rally testing framework);
- collects all the test results and processes them by Zipkin tracer;
- puts together a benchmarking report and stores it on the machine Rally was lauched on.
- Orchestrator, which is the central component of the system. It uses the Deploy Engine to run control and compute nodes and to launch an OpenStack distribution and, after that, calls the Benchmarking Tool to start the benchmarking process.
To dive deeper into the architectural concepts of Rally, see Rally architecture for developers.
Interesting results of Rally work
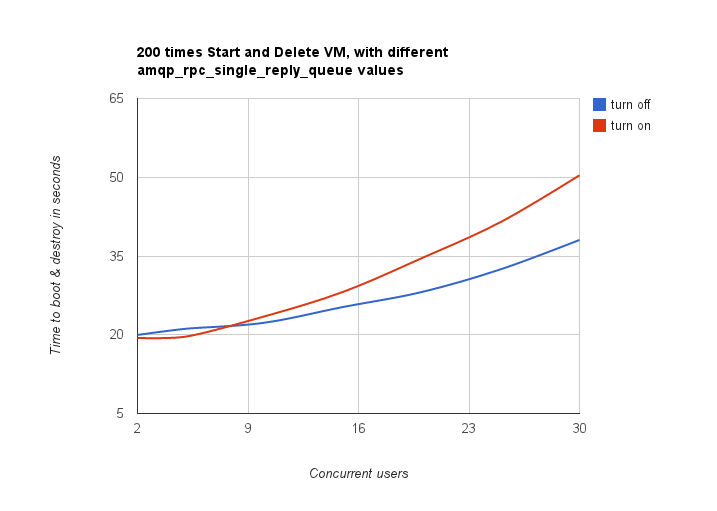
How influence amqp_rpc_single_reply_queue on performance
We used NovaServers.boot_and_destroy scenario, and get next results:
So probably we should get rid of such config options?
How To
- Rally installation
- How to use Rally
- Available Deploy engines
- Available Server providers
- Available Benchmark scenarios
- Extend Rally functionality
- Rally Road Map
Links
Source
https://github.com/stackforge/rally
Pending Code Reviews
https://review.openstack.org/#/q/status:open+rally,n,z
Project space
Blueprints
active: http://blueprints.launchpad.net/rally
v1 base: https://blueprints.launchpad.net/rally/+spec/init
Bugs
https://bugs.launchpad.net/rally
IRC chat
server: freenode.net
chanel: #openstack-rally