Difference between revisions of "Jacket"
Okay22many (talk | contribs) (→How to unify the compute and block storage management?) |
Okay22many (talk | contribs) (→How to unify the compute and block storage management?) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
In common, there are two ways to unify the compute and block storage management. | In common, there are two ways to unify the compute and block storage management. | ||
| − | + | # One way is that Jacket project offers the standard nova-compute hypervisor drivers and cinder-volume drivers for AWS, Azure, VMware vCloud Director and so on. AWS, Azure and so on will be managed as the different hypervisors just like KVM, Xen and so on. | |
This solution has the following weaknesses: | This solution has the following weaknesses: | ||
| − | + | * Only one account in the provider cloud can be used as the static configuration in nova-compute and cinder-volume driver because the standard nova-compute and cinder-volume can’t offer the restful API. When users want to modify the manage account, they must modify the static configuration and restart nova-compute and cinder-volume, and they can’t use the provider cloud through OpenStack. | |
| − | Only one account in the provider cloud can be used as the static configuration in nova-compute and cinder-volume driver because the standard nova-compute and cinder-volume can’t offer the restful API. When users want to modify the manage account, they must modify the static configuration and restart nova-compute and cinder-volume, and they can’t use the provider cloud through OpenStack | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * In the other way, Jacket will be an independent service to manage the different clouds with the unified restful APIs. And there will be only one nova-compute and cinder-volume driver for jacket | + | * The number of the resources in the provider cloud managed by OpenStack just is equal to the quota of the managed account. And all projects in OpenStack will share the resources. So, maybe each project just can use a little of resources. For example, the quota of an account in AWS just be allowed to create 20 VMs in one region by default. |
| + | |||
| + | * The associations of the flavors between OpenStack and the provider cloud just can be as the static configuration in nova-compute because of the same reason with the access account management. So, when the provider clouds add or update the flavors, users must update the configuration and restart nova-compute. | ||
| + | |||
| + | # In the other way, Jacket will be an independent service to manage the different clouds with the unified restful APIs. And there will be only one nova-compute and cinder-volume driver for jacket | ||
=== How to unify the network management? === | === How to unify the network management? === | ||
Revision as of 05:10, 8 March 2016
Contents
Overview
Now there are many people and enterprises using private clouds which are set up by OpenStack or VMware vCloud Director and so on, and the public clouds such as AWS, Azure and so on. Because the API models of each different cloud are different, users meet the following problems:
- High cost of learning: Users have to cost long time to learn how to use the new API of a new cloud which they will use.
- Large workload to deploy the business in a new cloud: When users want to deploy their business in a new cloud, there are a large workload to redevelop the business deployment tool or deploy the business manually using the API provided by the new cloud.
- Difficult to scale out the workload across the different clouds: There is no a unified resource management of the different clouds, users need develop a scaling across clouds tool which is not friendly because the tool need user to know the differences of the business configuration in different clouds.
The target of jacket project is to offer the standard OpenStack API model as the unified API model to manage the different clouds, such as AWS, Azure, private clouds based on Vmware vCloud Director or OpenStack and so on. And users can manage the different clouds just like one cloud.
Use case
Cross cloud deployment
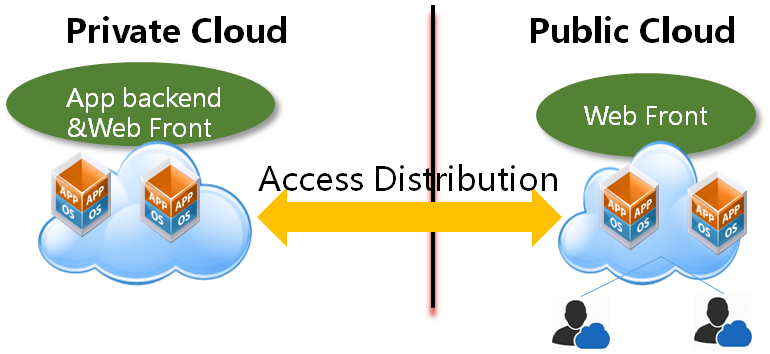
A typical web application is composed with 3 different tiers, the load balancer tier, the web front tier, and the app backend tier. Users have a private cloud based on OpenStack or VMware and so on, which just has less resources but more secure than public clouds. So they can use the standard OpenStack API to launch the web service's backend virtual machines in private cloud, launch the load balancer and web front virtual machines in the public clouds.
Cloud burst
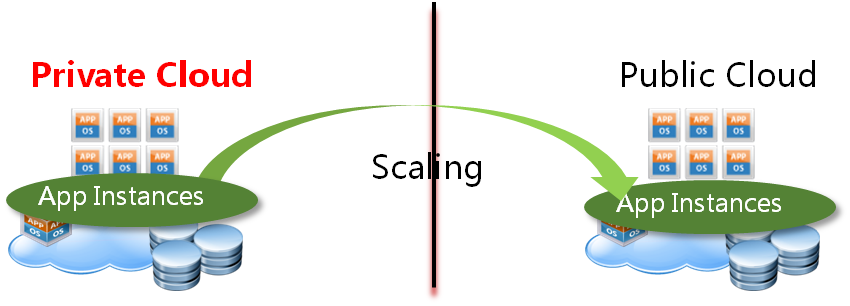
In some cases, user would not like to put anything in public cloud if not necessary. User would like to put all parts of the application in private cloud usually, and they would like to scale the web front end in case of there is a 'Cloud Burst' comes. For example, I have a online shopping mall in my private cloud, the system resource and internet bandwidth is enough in normal case. But there will have a bottleneck in big festival period, so I would like to scale out my application to public cloud in that period, and I would like to scale in my application back to private cloud after the big festival.
Challenges
How to unify the compute and block storage management?
In common, there are two ways to unify the compute and block storage management.
- One way is that Jacket project offers the standard nova-compute hypervisor drivers and cinder-volume drivers for AWS, Azure, VMware vCloud Director and so on. AWS, Azure and so on will be managed as the different hypervisors just like KVM, Xen and so on.
This solution has the following weaknesses:
- Only one account in the provider cloud can be used as the static configuration in nova-compute and cinder-volume driver because the standard nova-compute and cinder-volume can’t offer the restful API. When users want to modify the manage account, they must modify the static configuration and restart nova-compute and cinder-volume, and they can’t use the provider cloud through OpenStack.
- The number of the resources in the provider cloud managed by OpenStack just is equal to the quota of the managed account. And all projects in OpenStack will share the resources. So, maybe each project just can use a little of resources. For example, the quota of an account in AWS just be allowed to create 20 VMs in one region by default.
- The associations of the flavors between OpenStack and the provider cloud just can be as the static configuration in nova-compute because of the same reason with the access account management. So, when the provider clouds add or update the flavors, users must update the configuration and restart nova-compute.
- In the other way, Jacket will be an independent service to manage the different clouds with the unified restful APIs. And there will be only one nova-compute and cinder-volume driver for jacket
How to unify the network management?
There is a solution to use OpenStack Neutron to offer the unified network function through the overlay virtual network based on the provider clouds’ virtual network. This will be another project, Jacket project will not in include this part, and just focus on the unified compute and block storage management.
Architecture
Architecture layer 0
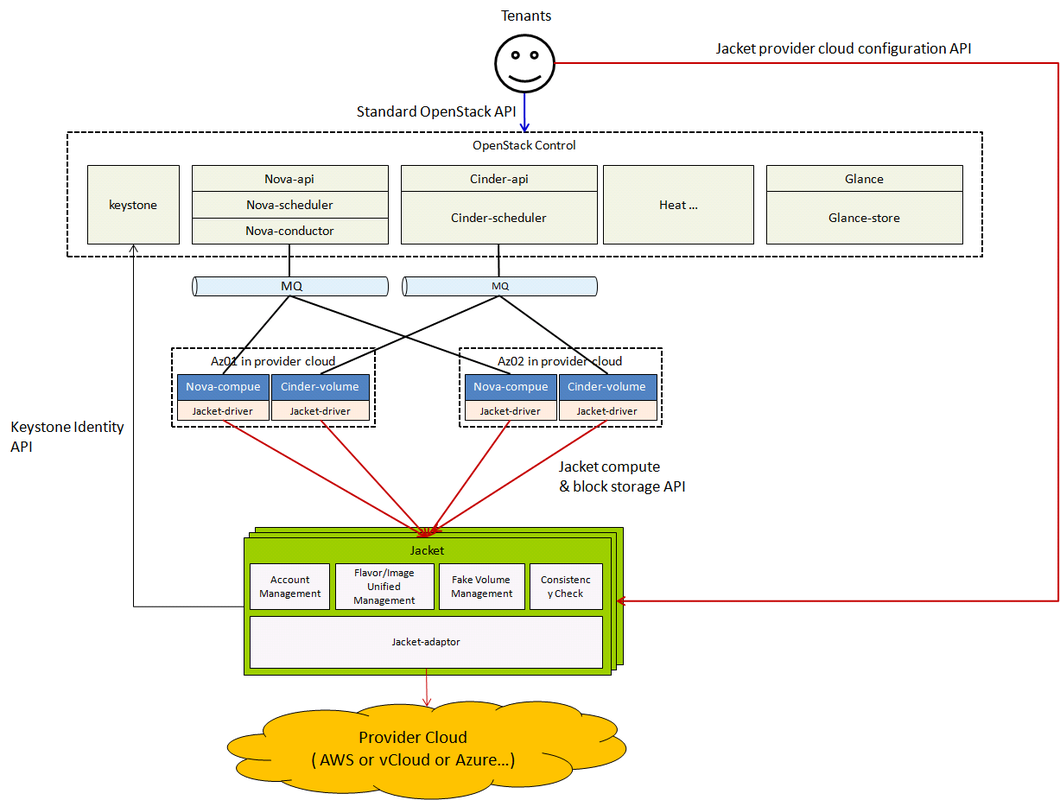
Jacket will offer the unified API models to manage the provider clouds. Jacket has the following functions:
- Account management: manage the accounts of the provider clouds, and the asociation between the projects in OpenStack and the accounts in the provider clouds.
- Flavor/image unified management: manage the associations between the flavors/images in OpenStack and the virtual machines flavors/images in the provider clouds.
- Fake volume management: offer the fake volume management to sheild the missing volume function in some provider clouds.
- Consistency check: check the consistency between the resources in OpenStack and the real resources in provider clouds.
Jacket can be deployed as a cluster. The Jacket cluster can manage multiply provider clouds at the same time, and we can also deploy multiply Jacket clusters in that each Jacket cluster just manage one provider cloud at the case of managing large scale virtual machines.
OpenStack will call Jacket through nova-compute/cinder-volume driver, just like calling Ironic to manage baremetal servers. There will be one nova-compute and cinder-volume to manage the resources in each availability zone of each provider cloud. Each nova-compute/cinder-volume has the different configuation of the name of the managed availability zone in the provider cloud.
Architecture layer1
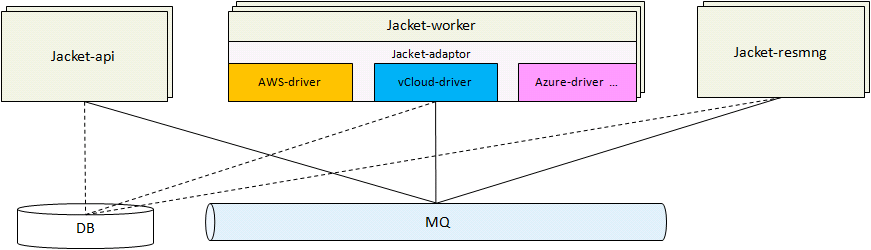
Jacket will have three modules, they are Jacket-api, Jacket-worker and Jacket-resmng.
- Jacket-api: offer the unified API models, its HA model is "active-active" just like nova-api and cinder-api.
- Jacket-worker: only this module contact with the provider clouds. It will receive the messages from Jacket-api and Jacket-resmng which will do something in the provider clouds, then it will contact with the provider clouds and handle the response from the provder clouds. It has a cloud adaptor framework, each provider cloud will offer a plugin to manage the provider cloud.
- Jacket-resmng: it will collect the resouces' status period and offer importting the existing resources in the provider clouds.
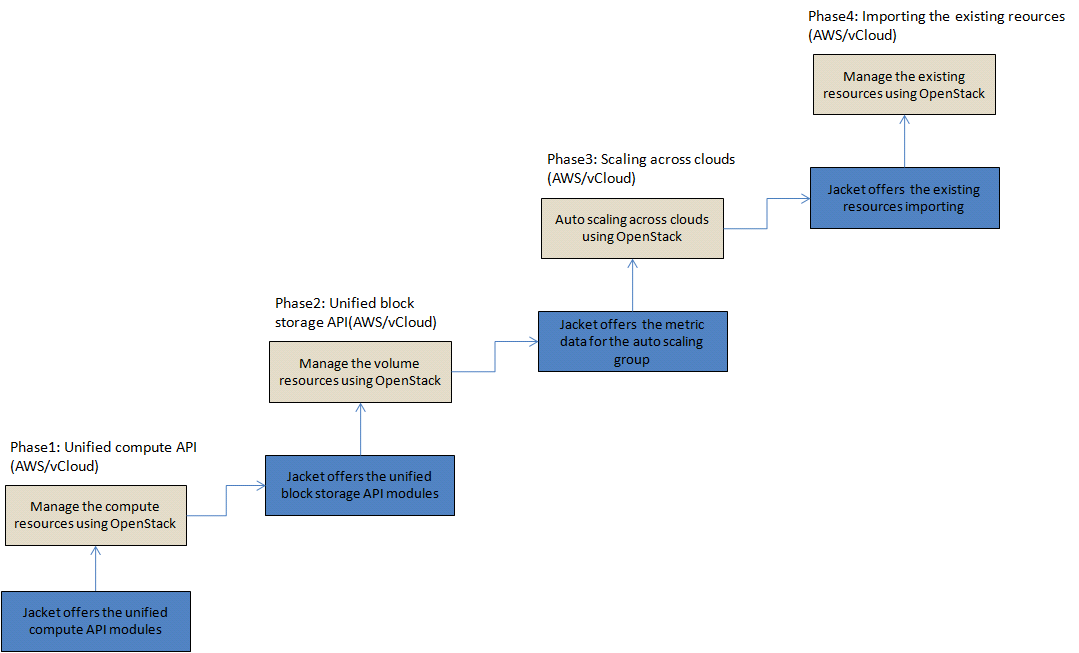
To do list
Phase1: Unified compute API(AWS/vCloud)
Phase2: Unified block storage API(AWS/vCloud)
Phase3: Scaling across clouds(AWS/vCloud)
Phase4: Importing the existing reources(AWS/vCloud)