FusionCompute
Contents
Overview
FusionCompute is a fully Huawei in-house developed computing virtualization software. FusionCompute provides the tuned high-performance and high reliabilities in VM instance provisioning, clustered resource pool management, and intelligent HA/FT scheduling.
Features
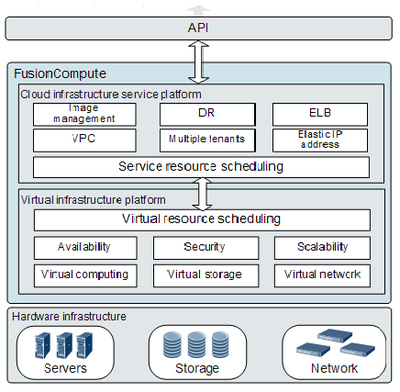
The overview of it can be illustrated as below:
Virtual Computing
- Server Virtualization
Bare Metal Architecture
CPU Virtualization
Memory Virtualization
Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) Passthrough
iNIC Passthrough
USB Passthrough
- VM Resource Management
VM life cycle management
VM template
CPU QoS
Memory QoS
Dynamic resource overcommitment for VMs
VM statistics
- Dynamic VM Resource Adjustment
Attaching virtual disks online/offline
Adding or deleting NICs offline
Adjusting the memory size online/offline
Adjusting the number of vCPUs online/offline
- Distributed Resource Scheduling and Power Management
Load balancing
Dynamic scheduling performed for energy saving
- VM Live Migration
Virtual Storage
- Virtual Image Management System
- Virtual Storage Management
Virtual image management system
Network file system
- Thin-Provisioning Virtual Storage
Storage device independent
Capacity monitoring
Disk space reclaiming
- VM Snapshot
- Storage Live Migration
Virtual Network
- Virtual NIC
Bandwidth control based on a network plane
Bandwidth control based on a virtual NIC
Bandwidth control based on a port group member port
- Elastic Virtual Switch
- Network I/O Control
- DVS
Topology
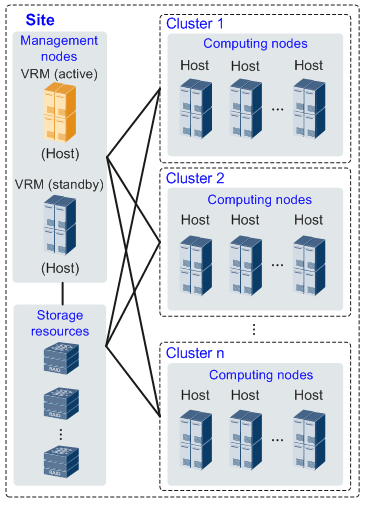
The figure below shows the logical nodes in the FusionCompute.
Modules
- VRM: Virtual Resource Management, core controller nodes of FusionCompute.
- Manages block storage resources in the cluster.
- Allocates private IP addresses for virtual machines (VMs) by using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
- Manages nodes in the computing cluster and maps physical computing resources to virtual computing resources.
- Manages network resources, such as IP addresses, virtual local area network (VLAN) numbers, security groups, and DHCP severs in the cluster and allocates private IP addresses to non-VPC VMs.
- Manages the life cycle of VMs in the cluster and distributes and migrates VMs across CNAs.
- Dynamically adjusts resources in the cluster.
- Implements centralized management of virtual resources and user data and provides elastic computing, storage, and IP address services.
- Allows O&M engineers to remotely access the FusionCompute through a web interface to perform resource monitoring and management and view resource statistics reports.
- CNA: Computing Node Agent, deploys on each compute nodes.
- Implements the virtual computing function.
- Manages the VMs running on the CNA.
- Manages the computing, storage, and network resources of the CNA.
- IMGS: Image Storage.
- UVP: The hypervisor of Huawei FusionCompute based on SuSE.
How FusionCompute works with Nova?
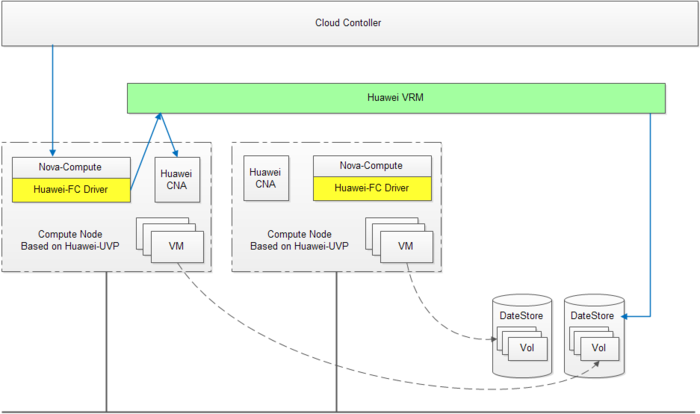
The basic architecture can be shown as below:
Note
- The package of nova-compute is deployed on the Huawei-CNA nodes.
- Nova-scheduler will select the suitable compute-hosts based on the reported resource as usual.
- Nova won't communicate with Huawei-VRM directly, the Huawei-FC Driver will be the bridge between them.
Example
Let's give an example for creating an instance:
1. Nova API receives a request for creating.
2. Nova Scheduler chooses a suitable host based on configure as usual.
3. Nova Compute receives the request, gets IP/mac info from neutron, and calls the spawn() on Huawei-FC Driver.
4. The Huawei-FC Driver sends the request to Huawei-VRM from the CNA node.
5. The Huawei-VRM choose the last node, and starts to create instance.
Deployment & Configure
Drafting