Difference between revisions of "FusionCompute"
(→Overview) |
(→Overview) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
=== Virtual Computing === | === Virtual Computing === | ||
| − | Server Virtualization | + | Server Virtualization (Bare Metal Architecture, CPU Virtualization , Memory Virtualization, Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) Passthrough, iNIC Passthrough, USB Passthrough)<br/> |
| − | VM Resource Management | + | VM Resource Management (VM life cycle management, VM template, CPU QoS, Memory QoS, Dynamic resource overcommitment for VMs, VM statistics)<br/> |
| − | Dynamic VM Resource Adjustment | + | Dynamic VM Resource Adjustment (Attaching virtual disks online/offline, Adding or deleting NICs offline, Adjusting the memory size online/offline, Adjusting the number of vCPUs online/offline)<br/> |
| − | Distributed Resource Scheduling and Power Management | + | Distributed Resource Scheduling and Power Management (Load balancing, Dynamic scheduling performed for energy saving)<br/> |
| − | VM Live Migration | + | VM Live Migration<br/> |
=== Virtual Storage === | === Virtual Storage === | ||
| − | Virtual Image Management System | + | Virtual Image Management System<br/> |
| − | Virtual Storage Management | + | Virtual Storage Management (Virtual image management system, Network file system)<br/> |
| − | Thin-Provisioning Virtual Storage | + | Thin-Provisioning Virtual Storage (Storage device independent, Capacity monitoring, Disk space reclaiming)<br/> |
| − | VM Snapshot | + | VM Snapshot<br/> |
| − | Storage Live Migration | + | Storage Live Migration<br/> |
=== Virtual Network === | === Virtual Network === | ||
| − | Virtual NIC | + | Virtual NIC (Bandwidth control based on a network plane, Bandwidth control based on a virtual NIC, Bandwidth control based on a port group member port)<br/> |
| − | Elastic Virtual Switch | + | Elastic Virtual Switch<br/> |
| − | Network I/O Control | + | Network I/O Control<br/> |
| − | DVS | + | DVS<br/> |
== Topology == | == Topology == | ||
Revision as of 09:38, 9 December 2013
Contents
Overview
FusionCompute is a fully Huawei in-house developed computing virtualization software. FusionCompute provides the tuned high-performance and high reliabilities in VM instance provisioning, clustered resource pool management, and intelligent HA/FT scheduling.
Features
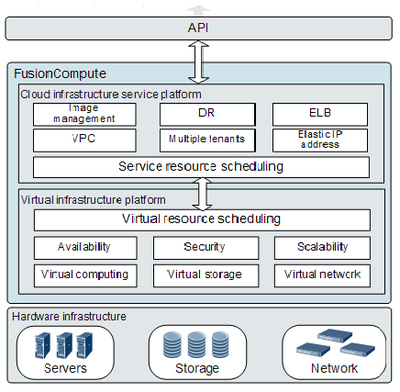
The overview of it can be illustrated as below:
Virtual Computing
Server Virtualization (Bare Metal Architecture, CPU Virtualization , Memory Virtualization, Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) Passthrough, iNIC Passthrough, USB Passthrough)
VM Resource Management (VM life cycle management, VM template, CPU QoS, Memory QoS, Dynamic resource overcommitment for VMs, VM statistics)
Dynamic VM Resource Adjustment (Attaching virtual disks online/offline, Adding or deleting NICs offline, Adjusting the memory size online/offline, Adjusting the number of vCPUs online/offline)
Distributed Resource Scheduling and Power Management (Load balancing, Dynamic scheduling performed for energy saving)
VM Live Migration
Virtual Storage
Virtual Image Management System
Virtual Storage Management (Virtual image management system, Network file system)
Thin-Provisioning Virtual Storage (Storage device independent, Capacity monitoring, Disk space reclaiming)
VM Snapshot
Storage Live Migration
Virtual Network
Virtual NIC (Bandwidth control based on a network plane, Bandwidth control based on a virtual NIC, Bandwidth control based on a port group member port)
Elastic Virtual Switch
Network I/O Control
DVS
Topology
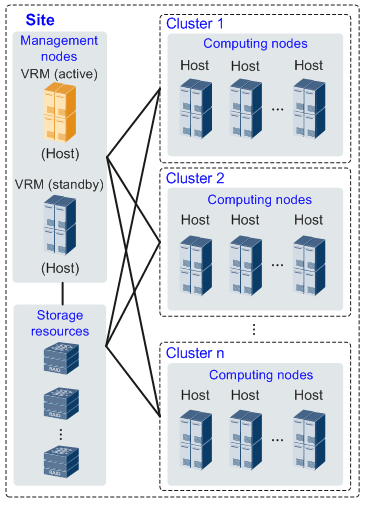
The figure below shows the logical nodes in the FusionCompute.
Modules
- VRM: Virtual Resource Management, core controller nodes of FusionCompute.
- Manages block storage resources in the cluster.
- Allocates private IP addresses for virtual machines (VMs) by using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
- Manages nodes in the computing cluster and maps physical computing resources to virtual computing resources.
- Manages network resources, such as IP addresses, virtual local area network (VLAN) numbers, security groups, and DHCP severs in the cluster and allocates private IP addresses to non-VPC VMs.
- Manages the life cycle of VMs in the cluster and distributes and migrates VMs across CNAs.
- Dynamically adjusts resources in the cluster.
- Implements centralized management of virtual resources and user data and provides elastic computing, storage, and IP address services.
- Allows O&M engineers to remotely access the FusionCompute through a web interface to perform resource monitoring and management and view resource statistics reports.
- CNA: Computing Node Agent, deploys on each compute nodes.
- Implements the virtual computing function.
- Manages the VMs running on the CNA.
- Manages the computing, storage, and network resources of the CNA.
- IMGS: Image Storage.
- UVP: The hypervisor of Huawei FusionCompute based on SuSE.
How FusionCompute works with Nova?
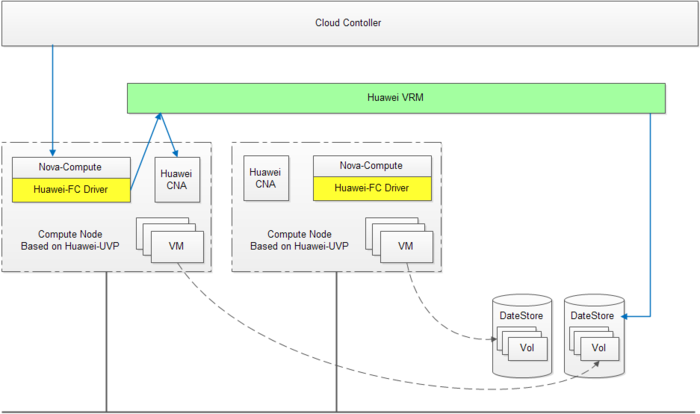
The basic architecture can be shown as below:
Note
- The package of nova-compute is deployed on the Huawei-CNA nodes.
- Nova-scheduler will select the suitable compute-hosts based on the reported resource as usual.
- Nova won't communicate with Huawei-VRM directly, the Huawei-FC Driver will be the bridge between them.
Example
Let's give an example for creating an instance:
1. Nova API receives a request for creating.
2. Nova Scheduler chooses a suitable host based on configure as usual.
3. Nova Compute receives the request, gets IP/mac info from neutron, and calls the spawn() on Huawei-FC Driver.
4. The Huawei-FC Driver sends the request to Huawei-VRM from the CNA node.
5. The Huawei-VRM choose the last node, and starts to create instance.
Deployment & Configure
Drafting