Difference between revisions of "DomainQuotaManagementAndEnforcement"
Yehia-beyh (talk | contribs) (→Usage Tracking and Limit Checking) |
m |
||
| (43 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | * '''Launchpad Entry''': [https://blueprints.launchpad.net/keystone/+spec/domain-quota-management-and-enforcement Domain Quota Management] | ||
| + | * '''Created''': 03 March 2013 | ||
| + | * '''Contributors''': [https://launchpad.net/~yehia-beyh Yehia Beyh], [https://launchpad.net/~glaucimar-aguiar Glaucimar Aguiar ], [https://launchpad.net/~tiago-martins Tiago Martins], [https://blueprints.launchpad.net/~the-akshat Akshat Kakkar] [https://launchpad.net/~ulrich-schwickerath Ulrich Schwickerath], | ||
| + | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| − | In Keystone v3 (Grizzly release), | + | In Keystone v3 (Grizzly release), Domains encapsulates users and projects into logical entities that can represent accounts, organizations, etc. Currently there is no capability or mechanism to manage or enforce quotas at domain level. Assigning or updating quota values or limits to a domain will allow the cloud administrator to evaluate domain lists and consumption. In order to achieve these capabilities it will be required to implement quota management for Keystone domains. |
| + | The goal of this blueprint is to support quotas at the OpenStack Domain level. The design of the feature models, as far as possible, the style of project quotas. | ||
| + | This blueprint is a contribution from CERN, BARC and Hewlett-Packard. | ||
| − | |||
== Openstack Quotas == | == Openstack Quotas == | ||
| − | + | Today OpenStack services make usage of quotas to limit the project resources. | |
| + | For example, the “Instances” quota represents the number of instances that can be created in a project. The table below summarizes the existing project quotas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! quotas !! type !! default values !! description | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.instances || reservable|| 10|| number of instances allowed per project | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.cores|| reservable|| 20|| number of instance cores allowed per project | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.ram || reservable || 50*1024|| megabytes of instance ram allowed per project | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.floating_ips || reservable || 10 || number of floating ips allowed per project | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.fixed_ips|| reservable|| -1 || number of fixed ips allowed per project | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.metadata_items|| absolute || 128|| number of metadata items allowed per instance | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.injected_files || absolute|| 5 || number of injected files allowed | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.injected_files_content_bytes|| absolute || 10*1024 || number of bytes allowed per injected file | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.injected_file_path_bytes || absolute|| 255 || number of bytes allowed per injected file path | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.security_groups || reservable || 10 || number of security groups per project | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.security_groups_rules || countable || 20 || number of security rules per security group | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | nova.key_pairs|| countable || 100 || number of key pairs per user | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | cinder.volumes || reservable || 10 || number of volumes allowed per project | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | cinder.snapshots || reservable || 10 || number of volume snapshots allowed per project | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | cinder.gigabytes || reservable || 1000 || number of volume gigabytes (snapshots are also included) per project | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | quantum.network || countable || 10 || Number of networks allowed per tenant | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | quantum.subnet || countable || 10 || Number of subnets allowed per tenant | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | quantum.port || countable || 50 || number of ports allowed per tenant | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == User Stories == | ||
| + | Domain Quotas might impact partitioned OpenStack deployments (regions, cells, etc). Here we consider only the impact on regions. These can be | ||
| + | # Per–Region domain quotas | ||
| + | # Across region domain quotas | ||
| + | |||
| + | The 1st approach works similar to the current implementation of quotas per project; in a multi-region scenario, the domain quotas are enforced by each service in a non-centralized fashion. The 2nd approach, a domain quota is shared dynamically among regions, e.g. if a service from a given region needs more quota than the others, it requests more quotas. | ||
| + | This blueprint addresses the per–region domain quotas. The user stories are listed below: | ||
| + | :* As a cloud administrator, I want to create a domain with default domain quotas | ||
| + | :* As a cloud/domain administrator, I want to see the domain quotas for a domain in a region | ||
| + | :* As a cloud administrator, I want to update the quotas for a domain in a region | ||
| + | :* As a cloud administrator, I want to delete the quotas for a domain in a region | ||
| − | + | Since quotas deals with sensible aspects of resource consumption, we identified the need to log the interactions of users when they manage domain quotas. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Design == |
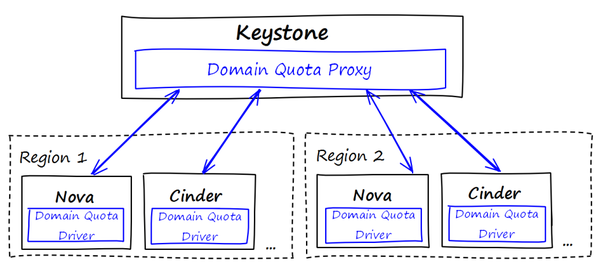
| − | + | Our proposal have 2 main blocks: one in keystone we are calling the Domain Quota Proxy (DQP), the other we are calling Domain Quota Driver (DQD). The DQP is responsible to give to user one point of domain quota management, so it acts as a proxy. The DQP is a discrete extesion that can be improved to serve as a single point of management for other quotas. The DQD is a piece of code located in the quota module of Nova, Cinder and Quantum projects, and it's designed in the same fashion as the other drivers present in such module. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:Domainquota.png|600x269px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Quota modules need to be refactored to add DQD. Also we should extend the services REST API to provide domain quotas usage to Domain Quota Proxy. The DQP is designed to be implemented as a discrete extension and not included in the default pipeline of Keystone. The Domain Quota Driver design is similar to the current quota driver from quota.py module, given the possibility to the user to option to use it or not; they will be responsible to enforce all quotas listed in the table above in the context of domains. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===REST API=== | ||
| + | This gives an option of '''getting''' quota for specific domain. | ||
| + | <pre><nowiki> | ||
| + | GET v3/{domain-id}/quotas | ||
| + | Content-Type application/json | ||
| + | Accept application/json | ||
| + | </nowiki></pre> | ||
| + | Request: | ||
| + | <pre><nowiki> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "quotas": { | ||
| + | "region": "regionOne", | ||
| + | "services": [ | ||
| + | "nova", | ||
| + | "cinder" | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </nowiki></pre> | ||
| + | Normal Response Code: 200<br/> | ||
| + | Error Response Codes: Unauthorized (401), Not Found (404)<br/> | ||
| + | Response:<br/> | ||
| + | <pre><nowiki> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "quotas": [ | ||
| + | [ | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "domain-id": "72415820-8b69-11e0-9b19-734f6acf67565", | ||
| + | "region": "RegionOne" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "nova": { | ||
| + | "instances": 10, | ||
| + | "cores": 20, | ||
| + | "ram": 1024, | ||
| + | "fixed_ips": -1, | ||
| + | "floating_ips": 10, | ||
| + | "metada_items": 128, | ||
| + | "injected_files": 5, | ||
| + | "injected_files_content_bytes": 1024, | ||
| + | "injected_file_path_bytes": 255, | ||
| + | "security_groups": 10, | ||
| + | "security_groups_rules": 20, | ||
| + | "key_pairs": 100 | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "cinder": { | ||
| + | "volumes": 20, | ||
| + | "snapshots": 10, | ||
| + | "gigabytes": 2048 | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </nowiki></pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This gives an option of '''updating''' quota for specific domain. | ||
| + | <pre><nowiki> | ||
| + | POST v3/{domain-id}/quotas | ||
| + | Content-Type application/json | ||
| + | Accept application/json | ||
| + | </nowiki></pre> | ||
| + | Request | ||
| + | <pre><nowiki> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "quotas":{ | ||
| + | "region":"RegionOne", | ||
| + | "nova":{ | ||
| + | "floating_ips": 30 | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }</nowiki></pre> | ||
| + | Normal Response Code: 200<br/> | ||
| + | Error Response Codes: Unauthorized (401), Not Found (404)<br/> | ||
| + | Response:<br/> | ||
| + | <pre><nowiki> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "quotas": [ | ||
| + | [ | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "domain-id": "72415820-8b69-11e0-9b19-734f6acf67565", | ||
| + | "region": "RegionOne" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "nova": { | ||
| + | "instances": 10, | ||
| + | "cores": 20, | ||
| + | "ram": 1024, | ||
| + | "fixed_ips": -1, | ||
| + | "floating_ips": 30, | ||
| + | "metada_items": 128, | ||
| + | "injected_files": 5, | ||
| + | "injected_files_content_bytes": 1024, | ||
| + | "injected_file_path_bytes": 255, | ||
| + | "security_groups": 10, | ||
| + | "security_groups_rules": 20, | ||
| + | "key_pairs": 100 | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </nowiki></pre> | ||
| − | + | This gives an option of '''deleting''' quota for specific domain. | |
| + | <pre><nowiki> | ||
| + | DELETE v3/{domain-id}/quotas | ||
| + | Content-Type application/json | ||
| + | Accept application/json | ||
| + | </nowiki></pre> | ||
| + | Request: | ||
| + | <pre><nowiki> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "quotas": { | ||
| + | "region": "regionOne", | ||
| + | "services": [ | ||
| + | "nova", | ||
| + | "cinder" | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </nowiki></pre> | ||
| + | Normal Response Code: 200<br/> | ||
| + | Error Response Codes: Unauthorized (401), Not Found (404)<br/> | ||
| + | Response:<br/> | ||
| + | <pre><nowiki> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "quotas": [ | ||
| + | [ | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "domain-id": "72415820-8b69-11e0-9b19-734f6acf67565", | ||
| + | "region": "RegionOne" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "nova": { | ||
| + | "instances": 10, | ||
| + | "cores": 20, | ||
| + | "ram": 1024, | ||
| + | "fixed_ips": -1, | ||
| + | "floating_ips": 10, | ||
| + | "metada_items": 128, | ||
| + | "injected_files": 5, | ||
| + | "injected_files_content_bytes": 1024, | ||
| + | "injected_file_path_bytes": 255, | ||
| + | "security_groups": 10, | ||
| + | "security_groups_rules": 20, | ||
| + | "key_pairs": 100 | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | "cinder": { | ||
| + | "volumes": 20, | ||
| + | "snapshots": 10, | ||
| + | "gigabytes": 2048 | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </nowiki></pre> | ||
| − | + | == Implementation == | |
| + | Tables are made generic enough so as to accommodate quotas for any resource of any service. 'quotas' table is capable enough to store quota for any entity (and not just domain). Entity for which a quota is set is called as child in generic terms. Entity responsible for managing quota of a child is called parent. A child and a parent, need not be described just by a single field like user-id alone. There can be multiple fields (like user-id, role, project-id, etc.) and its values which in combination describes a child or a parent. This can be seen as best represented in general by a dictionary. For simple DB implementation, it is suggested to store this dictionary as separate key-value data in separate tables. These tables are 'child_field_data' and 'parent_field_data' tables. | ||
| − | + | Details of fields of various DB tables is mentioned below, | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Quota Table''' | |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Column || Description |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | id || primary key | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | resource|| resource name | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ceiling||absolute quota limit | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | available||indicates available quota. Calculated as 'ceiling' – (resources used by corresponding child ) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | created_at||time at which the record is created | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | created_by||dictionary having minimum keys as user and role. This indicates who created the record. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | closed_at||time at which the record is created | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | closed_by||dictionary having minimum keys as user and role.. This indicates who closed the record. |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | '''Child_Field_Data Table''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Column || Description |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | id || primary key |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | quota_id || foreign key to quotas table. This helps in getting the quota for a child mentioned in this table. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | key || name of an attribute of child, like user-id, role-id, etc. | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | value || value of the attribute of child. |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | '''Parent_Field_Data Table''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Column || Description |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | id || primary key |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | quota_id || foreign key to quota table. This helps in getting the child information managed by the parent mentioned in this table (or vice-versa). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | key || name of an attribute of parent, like user-id, role-id, etc. | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | value || value of the attribute of parent. |
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | For history tracking, updates done in table <<nowiki />quota will be stored in the corresponding history table h_quota.<br/> | |
== Open Stack Quota References == | == Open Stack Quota References == | ||
Latest revision as of 16:12, 17 October 2013
- Launchpad Entry: Domain Quota Management
- Created: 03 March 2013
- Contributors: Yehia Beyh, Glaucimar Aguiar , Tiago Martins, Akshat Kakkar Ulrich Schwickerath,
Contents
Introduction
In Keystone v3 (Grizzly release), Domains encapsulates users and projects into logical entities that can represent accounts, organizations, etc. Currently there is no capability or mechanism to manage or enforce quotas at domain level. Assigning or updating quota values or limits to a domain will allow the cloud administrator to evaluate domain lists and consumption. In order to achieve these capabilities it will be required to implement quota management for Keystone domains. The goal of this blueprint is to support quotas at the OpenStack Domain level. The design of the feature models, as far as possible, the style of project quotas. This blueprint is a contribution from CERN, BARC and Hewlett-Packard.
Openstack Quotas
Today OpenStack services make usage of quotas to limit the project resources. For example, the “Instances” quota represents the number of instances that can be created in a project. The table below summarizes the existing project quotas.
| quotas | type | default values | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nova.instances | reservable | 10 | number of instances allowed per project |
| nova.cores | reservable | 20 | number of instance cores allowed per project |
| nova.ram | reservable | 50*1024 | megabytes of instance ram allowed per project |
| nova.floating_ips | reservable | 10 | number of floating ips allowed per project |
| nova.fixed_ips | reservable | -1 | number of fixed ips allowed per project |
| nova.metadata_items | absolute | 128 | number of metadata items allowed per instance |
| nova.injected_files | absolute | 5 | number of injected files allowed |
| nova.injected_files_content_bytes | absolute | 10*1024 | number of bytes allowed per injected file |
| nova.injected_file_path_bytes | absolute | 255 | number of bytes allowed per injected file path |
| nova.security_groups | reservable | 10 | number of security groups per project |
| nova.security_groups_rules | countable | 20 | number of security rules per security group |
| nova.key_pairs | countable | 100 | number of key pairs per user |
| cinder.volumes | reservable | 10 | number of volumes allowed per project |
| cinder.snapshots | reservable | 10 | number of volume snapshots allowed per project |
| cinder.gigabytes | reservable | 1000 | number of volume gigabytes (snapshots are also included) per project |
| quantum.network | countable | 10 | Number of networks allowed per tenant |
| quantum.subnet | countable | 10 | Number of subnets allowed per tenant |
| quantum.port | countable | 50 | number of ports allowed per tenant |
User Stories
Domain Quotas might impact partitioned OpenStack deployments (regions, cells, etc). Here we consider only the impact on regions. These can be
- Per–Region domain quotas
- Across region domain quotas
The 1st approach works similar to the current implementation of quotas per project; in a multi-region scenario, the domain quotas are enforced by each service in a non-centralized fashion. The 2nd approach, a domain quota is shared dynamically among regions, e.g. if a service from a given region needs more quota than the others, it requests more quotas. This blueprint addresses the per–region domain quotas. The user stories are listed below:
- As a cloud administrator, I want to create a domain with default domain quotas
- As a cloud/domain administrator, I want to see the domain quotas for a domain in a region
- As a cloud administrator, I want to update the quotas for a domain in a region
- As a cloud administrator, I want to delete the quotas for a domain in a region
Since quotas deals with sensible aspects of resource consumption, we identified the need to log the interactions of users when they manage domain quotas.
Design
Our proposal have 2 main blocks: one in keystone we are calling the Domain Quota Proxy (DQP), the other we are calling Domain Quota Driver (DQD). The DQP is responsible to give to user one point of domain quota management, so it acts as a proxy. The DQP is a discrete extesion that can be improved to serve as a single point of management for other quotas. The DQD is a piece of code located in the quota module of Nova, Cinder and Quantum projects, and it's designed in the same fashion as the other drivers present in such module.
Quota modules need to be refactored to add DQD. Also we should extend the services REST API to provide domain quotas usage to Domain Quota Proxy. The DQP is designed to be implemented as a discrete extension and not included in the default pipeline of Keystone. The Domain Quota Driver design is similar to the current quota driver from quota.py module, given the possibility to the user to option to use it or not; they will be responsible to enforce all quotas listed in the table above in the context of domains.
REST API
This gives an option of getting quota for specific domain.
GET v3/{domain-id}/quotas
Content-Type application/json
Accept application/json
Request:
{
"quotas": {
"region": "regionOne",
"services": [
"nova",
"cinder"
]
}
}
Normal Response Code: 200
Error Response Codes: Unauthorized (401), Not Found (404)
Response:
{
"quotas": [
[
{
"domain-id": "72415820-8b69-11e0-9b19-734f6acf67565",
"region": "RegionOne"
},
{
"nova": {
"instances": 10,
"cores": 20,
"ram": 1024,
"fixed_ips": -1,
"floating_ips": 10,
"metada_items": 128,
"injected_files": 5,
"injected_files_content_bytes": 1024,
"injected_file_path_bytes": 255,
"security_groups": 10,
"security_groups_rules": 20,
"key_pairs": 100
},
"cinder": {
"volumes": 20,
"snapshots": 10,
"gigabytes": 2048
}
}
]
]
}
This gives an option of updating quota for specific domain.
POST v3/{domain-id}/quotas
Content-Type application/json
Accept application/json
Request
{
"quotas":{
"region":"RegionOne",
"nova":{
"floating_ips": 30
}
}
}
Normal Response Code: 200
Error Response Codes: Unauthorized (401), Not Found (404)
Response:
{
"quotas": [
[
{
"domain-id": "72415820-8b69-11e0-9b19-734f6acf67565",
"region": "RegionOne"
},
{
"nova": {
"instances": 10,
"cores": 20,
"ram": 1024,
"fixed_ips": -1,
"floating_ips": 30,
"metada_items": 128,
"injected_files": 5,
"injected_files_content_bytes": 1024,
"injected_file_path_bytes": 255,
"security_groups": 10,
"security_groups_rules": 20,
"key_pairs": 100
}
}
]
]
}
This gives an option of deleting quota for specific domain.
DELETE v3/{domain-id}/quotas
Content-Type application/json
Accept application/json
Request:
{
"quotas": {
"region": "regionOne",
"services": [
"nova",
"cinder"
]
}
}
Normal Response Code: 200
Error Response Codes: Unauthorized (401), Not Found (404)
Response:
{
"quotas": [
[
{
"domain-id": "72415820-8b69-11e0-9b19-734f6acf67565",
"region": "RegionOne"
},
{
"nova": {
"instances": 10,
"cores": 20,
"ram": 1024,
"fixed_ips": -1,
"floating_ips": 10,
"metada_items": 128,
"injected_files": 5,
"injected_files_content_bytes": 1024,
"injected_file_path_bytes": 255,
"security_groups": 10,
"security_groups_rules": 20,
"key_pairs": 100
},
"cinder": {
"volumes": 20,
"snapshots": 10,
"gigabytes": 2048
}
}
]
]
}
Implementation
Tables are made generic enough so as to accommodate quotas for any resource of any service. 'quotas' table is capable enough to store quota for any entity (and not just domain). Entity for which a quota is set is called as child in generic terms. Entity responsible for managing quota of a child is called parent. A child and a parent, need not be described just by a single field like user-id alone. There can be multiple fields (like user-id, role, project-id, etc.) and its values which in combination describes a child or a parent. This can be seen as best represented in general by a dictionary. For simple DB implementation, it is suggested to store this dictionary as separate key-value data in separate tables. These tables are 'child_field_data' and 'parent_field_data' tables.
Details of fields of various DB tables is mentioned below,
Quota Table
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| id | primary key |
| resource | resource name |
| ceiling | absolute quota limit |
| available | indicates available quota. Calculated as 'ceiling' – (resources used by corresponding child ) |
| created_at | time at which the record is created |
| created_by | dictionary having minimum keys as user and role. This indicates who created the record. |
| closed_at | time at which the record is created |
| closed_by | dictionary having minimum keys as user and role.. This indicates who closed the record. |
Child_Field_Data Table
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| id | primary key |
| quota_id | foreign key to quotas table. This helps in getting the quota for a child mentioned in this table. |
| key | name of an attribute of child, like user-id, role-id, etc. |
| value | value of the attribute of child. |
Parent_Field_Data Table
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| id | primary key |
| quota_id | foreign key to quota table. This helps in getting the child information managed by the parent mentioned in this table (or vice-versa). |
| key | name of an attribute of parent, like user-id, role-id, etc. |
| value | value of the attribute of parent. |
For history tracking, updates done in table <quota will be stored in the corresponding history table h_quota.
Open Stack Quota References
This is a list of URLs of work on quotas within OpenStack.