Celery
Celery Homepage http://celeryproject.org/
Contents
OVERVIEW
Celery is a Distributed Task Queue.
"Celery is an asynchronous task queue/job queue based on distributed message passing. It is focused on real-time operation, but supports scheduling as well. The execution units, called tasks, are executed concurrently on a single or more worker servers using multiprocessing, Eventlet, or gevent. Tasks can execute asynchronously (in the background) or synchronously (wait until ready)."
ARCHITECTURE
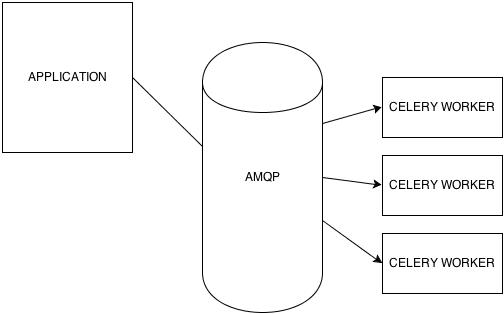
Celery works by asynchronously (or synchronously if designated) posting task objects to any AMQP - compliant message queue. (List of suggested implementations can be found here: http://docs.celeryproject.org/en/latest/getting-started/brokers/index.html). This is not a dedicated queue, so your queue can be hosted locally, on another box, in a different project, etc. The tasks now sitting on the queue are picked up by the next available listening celery worker. These workers, like the queue, can be hosted locally, or on an external host, or on multiple hosts. The worker will process and execute the task, then return the results up through the celery client and back into the application.
WORKERS
http://docs.celeryproject.org/en/latest/userguide/workers.html Celery workers are extremely efficient and customizable. Workers can set time-out for tasks (both before and during run-time), set concurrency levels, number of processes being run, and can even be set to autoscale. Workers can be assigned to specific queues and can be added to queues during run time.
DEBUGGING
http://docs.celeryproject.org/en/latest/userguide/monitoring.html
Celery allows for all sorts of debugging utilities.
QUEUES
As celery sends task through AMQP, you can use whatever tools your AMQP queue uses to examine its' contents.
WORKERS
Per individual worker, you can retrieve a dump of registered, currently executing, scheduled, and reserved tasks.
CLUSTERS
Per each celery cluster, you can examine the status of all nodes, find results of individual tasks, inspect active/registered/scheduled/reserved/revoked tasks, and see worker stats
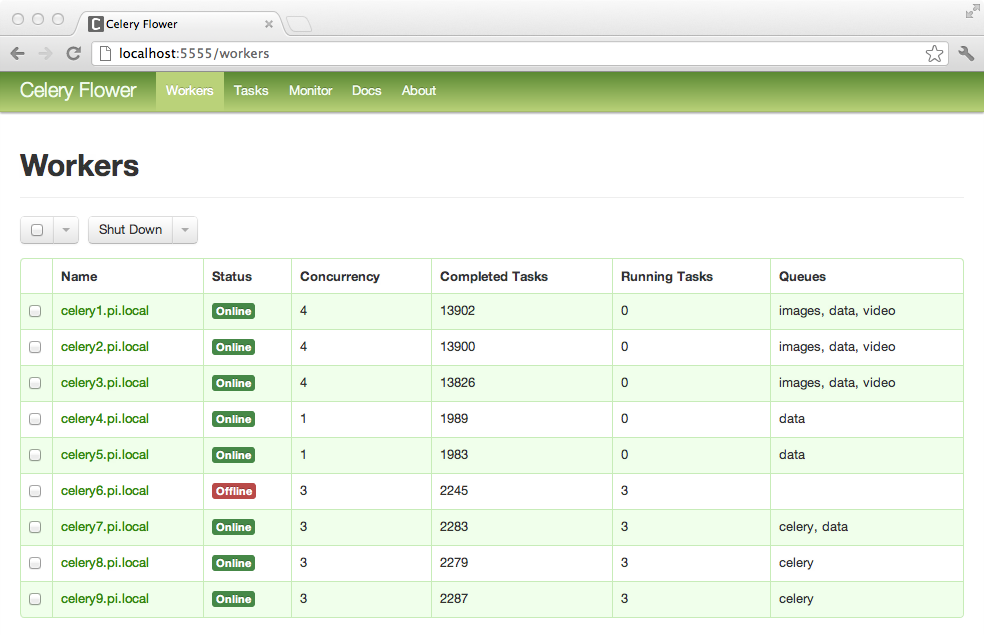
FLOWER
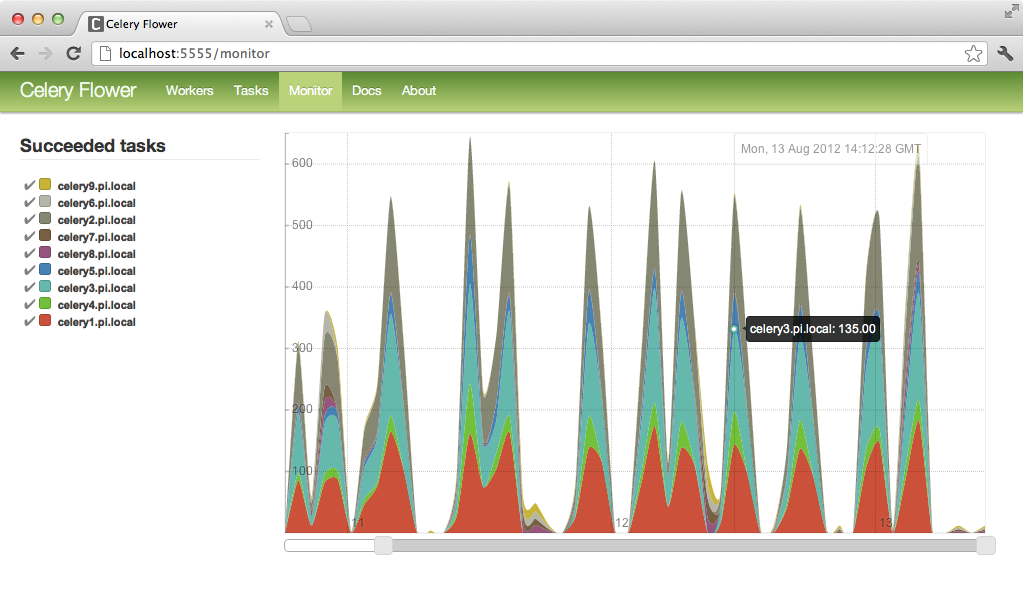
As this is a lot of information to process through logs (although completely do-able), Celery has provided a real-time web based monitor called Flower. Not only can you actively monitor tasks and their current status, but you can also modify workers and task during run-time (or after, or before).
Features
Real-time monitoring using Celery Events
- Task progress and history.
- Ability to show task details (arguments, start time, runtime, and more)
- Graphs and statistics
Remote Control
- View worker status and statistics.
- Shutdown and restart worker instances.
- Control worker pool size and autoscale settings.
- View and modify the queues a worker instance consumes from.
- View currently running tasks
- View scheduled tasks (ETA/countdown)
- View reserved and revoked tasks
- Apply time and rate limits
- Configuration viewer
- Revoke or terminate tasks
HTTP API