Difference between revisions of "Auto-scaling SIG/Theory of Auto-Scaling"
Joseph Davis (talk | contribs) (→Components of Auto-Scaling) |
Joseph Davis (talk | contribs) (→Components of Auto-Scaling) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
** Network Attached Storage | ** Network Attached Storage | ||
** Virtual Network Functions | ** Virtual Network Functions | ||
| − | * Monitoring Service | + | * Monitoring Service - either using an agent installed on the Scaling unit, or using a polling method to retrieve metrics |
** [https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Monasca Monasca] | ** [https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Monasca Monasca] | ||
** [https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Telemetry Ceilometer from the Telemetry project] | ** [https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Telemetry Ceilometer from the Telemetry project] | ||
Revision as of 23:29, 15 May 2019
Contents
Theory of Auto-Scaling
General Description
<fill in> <what is the scope of auto-scaling, how does it differ from self-healing, what does it have in common with self-healing>
Conceptual Diagram
Components of Auto-Scaling
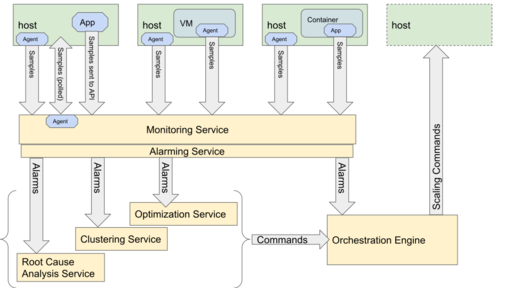
OpenStack offers a rich set of services to build, manage, orchestrate, and provision a cloud. This gives administrators some choices in how to best serve their customer's needs.
- Scaling units - There are a number of components that can be controlled with Auto-Scaling.
- Compute Host
- VM running on a Compute Host
- Container running on a Compute Host
- Network Attached Storage
- Virtual Network Functions
- Monitoring Service - either using an agent installed on the Scaling unit, or using a polling method to retrieve metrics
- Monasca
- Ceilometer from the Telemetry project
- Prometheus
- Alarming Service
- Monasca has a built in alarm thresholding service and notification service
- Aodh from the Telemetry project
- Decision Services - There are a number of services in OpenStack that can interpret metrics and alarms based on configured logic and produce commands to Orchestration Engines
- Congress
- Heat
- Vitrage
- Watcher
- Orchestration Engines
- Heat
- Senlin is a clustering engine for OpenStack, and can orchestrate auto-scaling
- Tacker
Considerations and Guidelines
- Monitoring takes resources, plan accordingly
- Avoid scaling too quickly or too often
- Don't expect instantaneous scaling (see above)
- Be aware of where the logic for scaling is (alarm thresholds, decision services)